Food can some people be recognized by the body as a foreign substance, against which the body can develop an immune response. The prevalence of food allergy is estimated at about 1% of the population, but in children it reaches 3% of the pediatric population.
Family history of food allergy and food diversification is very early risk factors for the development of food allergies while breastfeeding is a protective factor.
The clinical manifestations are variable from one patient to others :
Swelling of the lips, tongue, face and / or throat (angioedema), hives, rashes, itching, eczema, diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rhinitis, breathing difficulties, shock with risk of death sudden.
Urticaria food allergy to sunflower seeds.
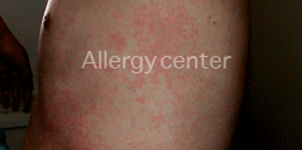
Hives in a 7 year old girl, with a polyallergie food.

Peri-oral dermatitis and cheilitis in a patient 12 years of age whose exploration was for a milk allergy.
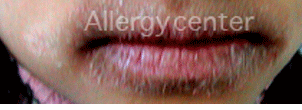
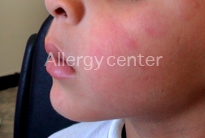
7 year old child, with swelling of the lips with asymmetric perioral rash after eating a hazelnut ice cream.
Skin tests were positive in native hazelnut.

Which foods are the main causes of food allergy ?
Any food ingested can be allergenic. But the most allergenic foods are:
Cow’s milk and hen’s egg in infants
Cow’s milk and hen’s egg and peanut in children
However Tunisian adults, it is seafood, fish and peanuts are the most incriminated.
RAST ( radioallergosorbent )
This is a blood looking for specific antibody sample . These blood tests are much less sensitive than skin tests and provocation tests .
The evolution of food allergies :
Food allergies are usually final , except for allergies to cow ‘s milk proteins and chicken egg disappear between 18 months and 2 years.
How to manage a food allergy ?
The best treatment for food allergy is preventive , based on the total eviction of the offending food . Beware of hidden allergens in other foods , so it is important not to ingest food whose composition is not known , and learn to read the labels of the products manufactured by the food industry .
Desensitization to cow’s milk or hen’s egg may be tempted to a specialist in children with persistent allergic to any of these foods and this beyond the usual age of healing.
Wearing an allergic map indicating the type of allergy , and an emergency kit containing epinephrine , avoids fatal in case of occurrence of anaphylactic shock.
Labial provocation test:
Is to deposit near the outer labial a drop of the allergen. The appearance of redness around the mouth or in the cheek can retain formal diagnosis without a provocation test orally.
Labial provocation test positive milk
Onset around 10 minutes after application of 5 drops of milk perioral erythema.
The provocation test by oral route:
In this test, the patient will ingest specialized environment and under strict medical supervision, the suspect food according to a standardized protocol and varies from one food to another.
The appearance of allergic manifestations can confirm the diagnosis.
Labial provocation test positive for fishing.
CENTRE TUNISIEN D'EXPLORATION DES MALADIES ALLERGIQUES
How to diagnose food allergy ?
The diagnosis of food allergy is relatively difficult. Guided by the examination, must be confirmed by additional tests :
The skin prick tests :
They will be made with native foods. Their positive and negative predictive values are very good.
Prick tests positive for native wheat flour in a patient 3 years followed for chronic diarrhea.
Colonoscopy: nonspecific inflammation.
Regression of diarrhea in exclusion diet flour.
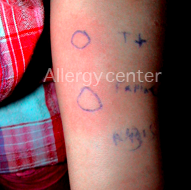
Prick tests positive for native white and egg yolk in an infant with lesions of atopic dermatitis refractory to symptomatic treatment.
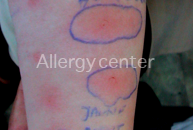
Positive skin tests to veal and mutton raw but negative cooked meat.
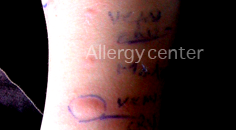
Patient of 34 years without previous history,presented with anaphylactic shock inaugural treated by adrenaline.
Her honey skin tests are positive.
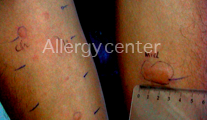
In cases where clinical reactions are delayed, patch testing native food should be performed.
Exclusion diets and reintroduction: food suspects are eliminated from the diet for two weeks. This should be accompanied by the disappearance of clinical manifestations. The recovery of the suspect food is accompanied by the reappearance of lesions. In case of severe manifestations, reintroduction can be done by specialized environment under strict medical supervision.
Labial provocation test:
Is to deposit near the outer labial a drop of the allergen. The appearance of redness around the mouth or in the cheek can retain formal diagnosis without a provocation test orally.
Labial provocation test positive milk
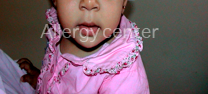
Onset around 10 minutes after application of 5 drops of milk perioral erythema.
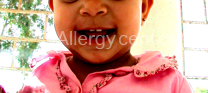
The provocation test by oral route:
In this test, the patient will ingest specialized environment and under strict medical supervision, the suspect food according to a standardized protocol and varies from one food to another.
The appearance of allergic manifestations can confirm the diagnosis.
Labial provocation test positive for fishing.
RAST ( radioallergosorbent )
This is a blood looking for specific antibody sample . These blood tests are much less sensitive than skin tests and provocation tests .
The evolution of food allergies :
Food allergies are usually final , except for allergies to cow ‘s milk proteins and chicken egg disappear between 18 months and 2 years.
How to manage a food allergy ?
The best treatment for food allergy is preventive , based on the total eviction of the offending food . Beware of hidden allergens in other foods , so it is important not to ingest food whose composition is not known , and learn to read the labels of the products manufactured by the food industry.
Desensitization to cow’s milk or hen’s egg may be tempted to a specialist in children with persistent allergic to any of these foods and this beyond the usual age of healing.
Wearing an allergic map indicating the type of allergy , and an emergency kit containing epinephrine , avoids fatal in case of occurrence of anaphylactic shock.